Hearing loss affects more than 48 million Americans (NIDCD, 2024). Despite how common it is, myths and unanswered questions often prevent people from seeking care. At Happy Hearing Clinic in Winchester, KY, we hear these questions every day—and we want to provide clear, evidence-based answers. This Hearing Loss FAQ will help you understand causes, treatments, and prevention strategies, while also addressing the stigma that surrounds hearing loss.
FAQ #1: Is hearing loss only a problem for older adults?
While hearing loss does become more common with age, it can affect people at any stage of life. Children may experience hearing loss due to ear infections or congenital conditions, teens and young adults may develop hearing problems from noise exposure, and adults of all ages may encounter hearing changes due to illness, injury, or genetics (WHO, 2024).
FAQ #2: What are the main causes of hearing loss?
Hearing loss can be classified into three categories: conductive, sensorineural, and mixed. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound cannot pass efficiently through the outer or middle ear—often due to earwax, infections, or fluid. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when the inner ear or auditory nerve is damaged—commonly from aging, noise exposure, or genetic conditions. Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both (CDC, 2024).
FAQ #3: Can hearing loss be treated?
Yes. Many causes of conductive hearing loss, such as earwax blockages or infections, can be treated medically. Sensorineural hearing loss is typically permanent, but hearing aids and cochlear implants can dramatically improve communication and quality of life. Early intervention leads to the best outcomes (AAA, 2024).
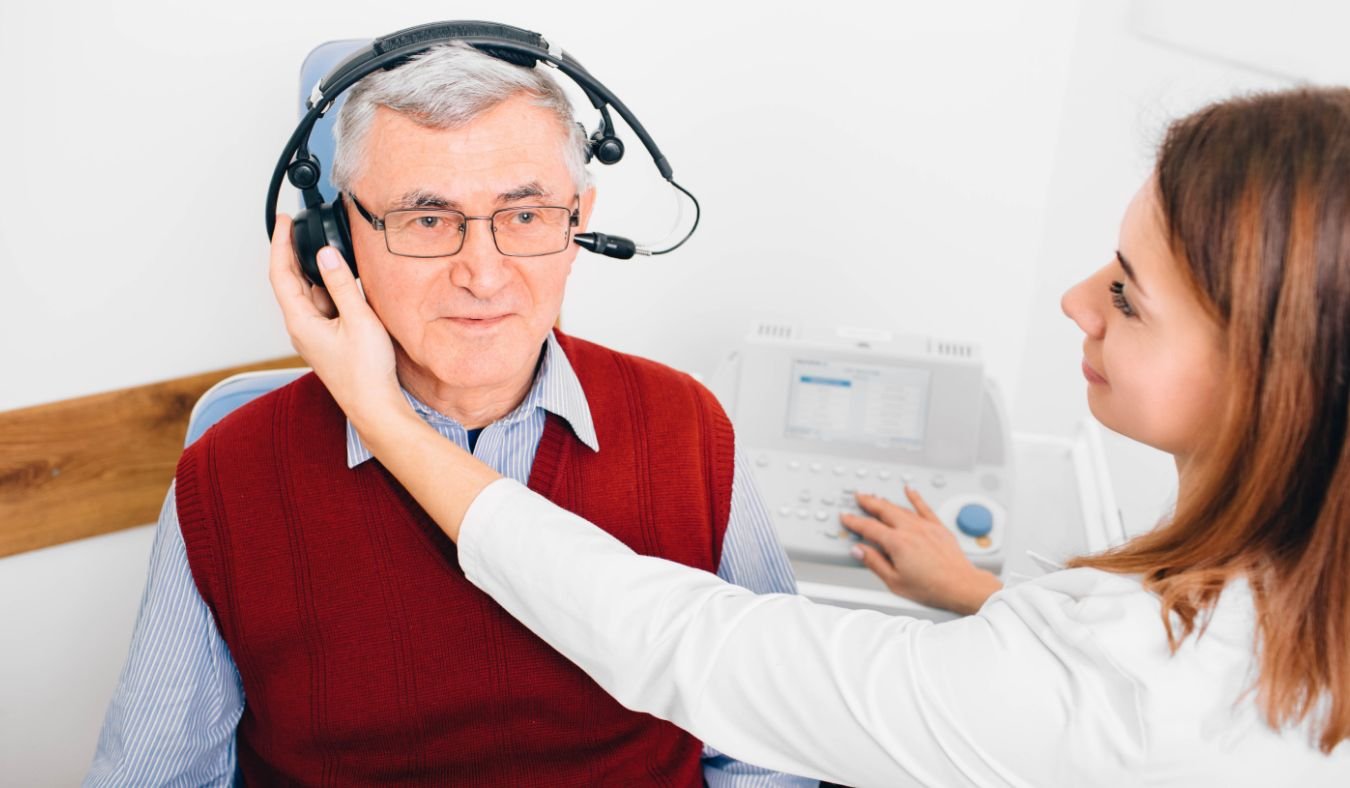
FAQ #4: How do I know if I have hearing loss?
Common signs include difficulty understanding speech, frequently asking people to repeat themselves, turning up the TV volume, or withdrawing from social activities. A comprehensive hearing evaluation by an audiologist is the only way to know for sure (NIDCD, 2024). Hearing Evaluations
FAQ #5: Are hearing aids really that effective?
Modern hearing aids are highly effective, discreet, and customizable. They amplify sounds in specific frequency ranges where hearing loss occurs and use advanced processing to reduce background noise. Many also connect to smartphones and TVs via Bluetooth, making them a powerful tool for everyday life (AAA, 2024).
FAQ #6: Isn’t hearing loss just an inconvenience?
No. Untreated hearing loss is linked to social isolation, depression, reduced job performance, and even cognitive decline, including dementia risk (WHO, 2024). Treating hearing loss helps maintain mental sharpness, relationships, and independence.
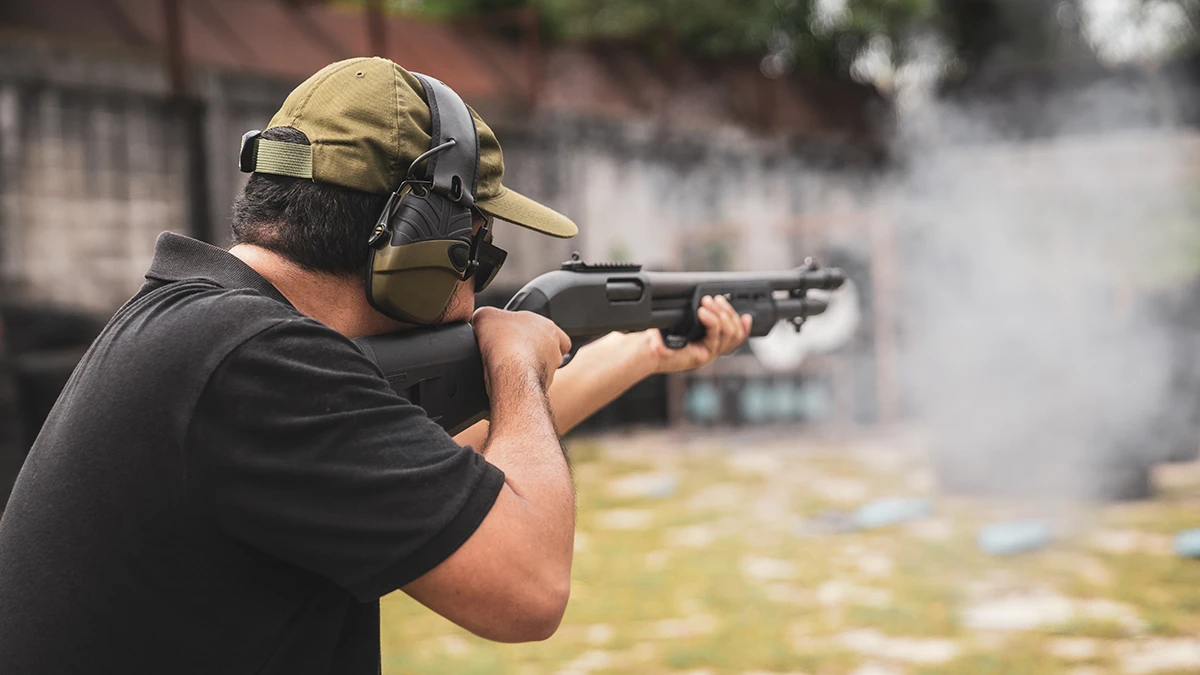
FAQ #7: Can noise cause permanent hearing loss?
Yes. Prolonged exposure to loud sounds—concerts, earbuds, machinery, or gunfire—can permanently damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear. Unlike other cells in the body, these do not regenerate. That’s why hearing protection is so important (CDC, 2024). Hearing Protection
FAQ #8: How common is hearing loss in the U.S.?
According to the NIDCD, approximately 15% of American adults (37.5 million people) report some trouble hearing. Globally, the WHO estimates over 1.5 billion people live with hearing loss, a number expected to grow significantly in coming decades (NIDCD, 2024; WHO, 2024).
FAQ #9: How often should I get my hearing tested?
Adults should have their hearing tested at least once every 3–5 years, and annually after age 50. Children should be screened regularly through pediatric check-ups and school programs. Anyone exposed to loud noise should schedule more frequent evaluations (AAA, 2024).
Conclusion
Hearing loss is common—but it doesn’t have to limit your life. With early testing, proper treatment, and ongoing support, you can protect your hearing and maintain a high quality of life. At Happy Hearing Clinic in Winchester, KY, we provide comprehensive evaluations, advanced hearing aid fittings, cochlear implant support, and custom hearing protection. If you have questions or concerns, let’s talk—we’re here to help you hear your best.
Schedule your evaluation today
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Hearing Loss.
https://www.cdc.gov/hearing
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. (2024). Quick
Statistics About Hearing.
https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/statistics/quick-statistics-hearing
World Health Organization. (2024). Deafness and hearing loss.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss
American Academy of Audiology. (2024). Hearing and Balance.
https://www.audiology.org/consumers-and-patients/hearing-and-balance/